This is a forever incomplete glossary of the realm of fungi to which we will continuously be adding terms, definitions and explanations. We encourage knowledge sharing and participation in uncovering or explaining the natural world.
To correct or help expand this glossary, please write to us at info@betterorganix.com or let us know in the comments below.
To help expand this glossary, please write to us at info@betterorganix.com.
Mycorrhizae
Fungi that has evolved in association with plants and creates symbiotic or semi-symbiotic (mildly pathogenic) relationships with plants and trees.
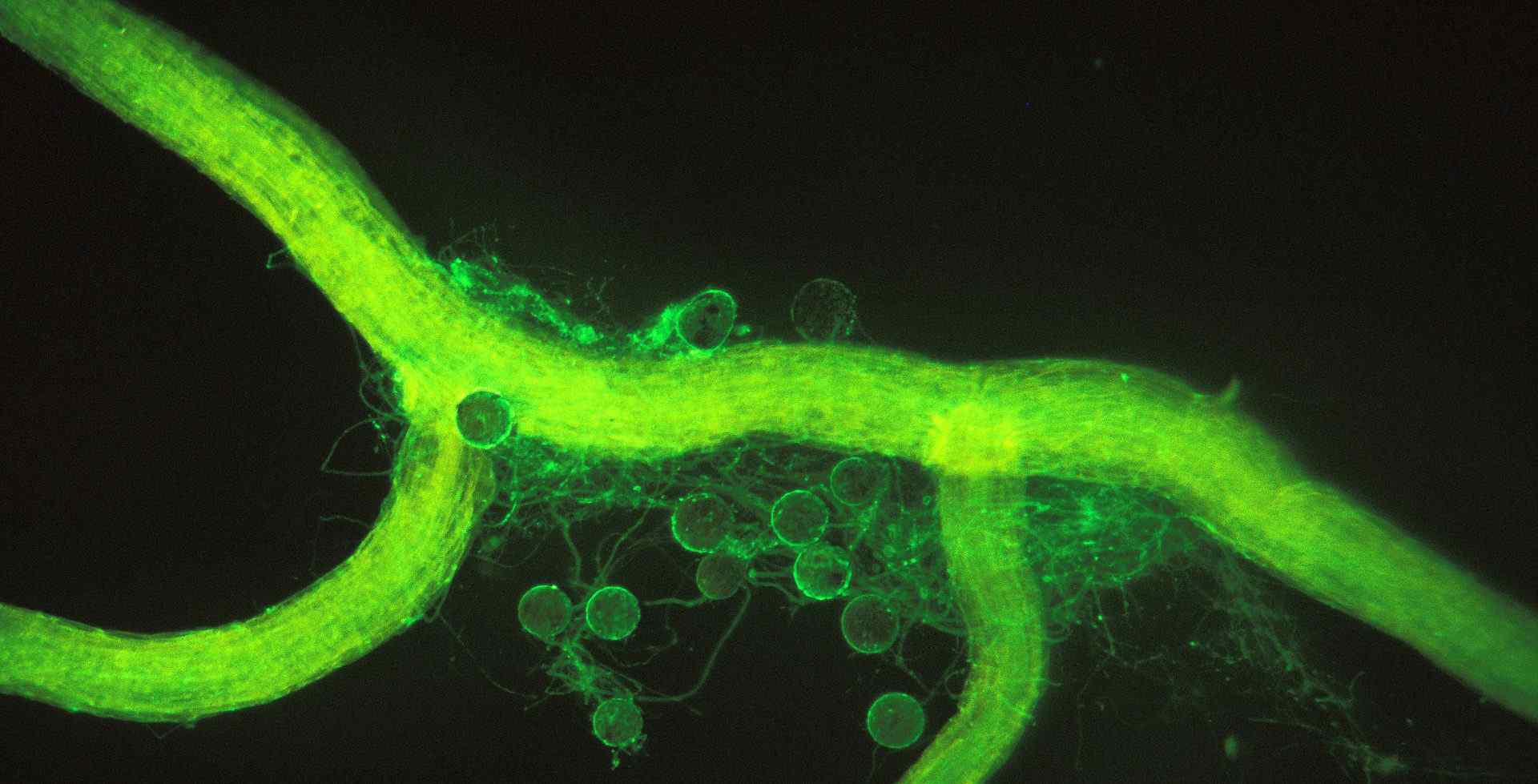
- Arbuscule
Highly branched structure produced by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inside the cell lumen of their host. A penetrating branch-like structure that is key to symbiotic nutrient and information exchange between the plant & the fungus.
- Arbuscular mycorrhiza
A widespread type of endomycorrhizal interactions involving fungi of the phylum Glomeromycota, the hyphae of which reach the root inner cortex & develop highly branched structures called arbuscules.
- Ascomycetes
A level of classification (called Phylum) of the fungi kingdom. It is best characterized by a microscopic sexual reproductive structure called the ascus, which is a single cell containing spores that are non-motile (meaning that they lack the ability to move independently). Ascomycetes also include macroscopic fungi that live in symbiosis with forest trees.
- Aseptate endophytes
Plant colonizing fungi with syncytial hyphae that lack transversal walls (septa).
- Basidiomycetes
Phylum of fungi kingdom the sexual reproduction of which is accomplished in club-shaped cells called basidia that bear external spores. Several basidiomycetes develop ectomycorrhizas.
- Ectomycorrhiza
Symbiosis between higher plants & fungi that belong to Asco- & Basidiomycetes, in which fungal hyphae surround the root tips & develop between epidermal cells but never enter the cell lumen.
- Endomycorrhiza
Group of mycorrhizal symbiosis involving fungal penetration inside living cells of the root epidermis & cortex.
- Extraradical mycelium
A hyphal network that develops in the rhizosphere, in which it absorbs inorganic nutrients that are transferred to the host plant through intraradical hyphae.
- Hyphopodium
It is a specialized hypha of a mycorrhizal fungus that forms arbuscules. Most commonly branched & swollen and is attached to the root epidermis before intracellular fungal penetration.
- Intraradical Hyphae
A network of hyphae from mycorrhizal fungi that colonizes the host root tissues.
- Metagenomics
Analysis of genetic material obtained from environmental samples.
- Nodulation (Nod) factors
Signalling molecules produced by nitrogen-fixing bacteria (rhizobia) & eliciting nodule initiation & bacterial uptake in the roots of legumes. They are lipochitooligosaccharides consisting of an acylated chitin oligomeric backbone carrying various functional group substitutions at the terminal or non-terminal residues.
- Pathogen
An organism that receives its nutrients from a host whilst causing a disease.
- Perifungal interface
The thin apoplastic compartment that surrounds each intracellular fungal structure inside plant tissues. The interface consists of plant cell wall components & is bordered by an invagination of the plant plasma membrane.
- Pre Symbiotic phase
The phase that precedes contact with the host plant in the life cycle of mycorrhizal fungi. In this phase fungal growth is not supported by plant provided nutrients.
- Saprotroph
A fungal organism that obtains nutrients from dead organic matter.